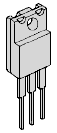|
|
BEAM Pieces is a BEAM Reference Library site.
Electrical part packages
The shapes of things to
come
|
|
|
|
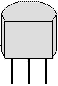 |
This package looks like a little "squished" plastic cylinder, with 3 leads. 1381* ICs come in this package, as do many transistors. |
|
|
|
This package has a thin metal backing for heat rejection (basically, it's a radiator). It's used, as you might suspect, for components that need to reject heat. We'll just see it used for voltage regulators like the 78M05. |
|
 (image courtesy of Solarbotics) |
DIPs are used for many "medium complexity" ICs. They have (as the name would suggest) two (dual) rows (in-line) of pins -- up to 20 pins total for the chips we'll be using. You can either solder directly to these pins, or plug your DIP IC into a socket, and solder to the socket's pins (use of a socket is generally preferred for a number of reasons). A DIP's pins are all numbered in a counter-clockwise fashion (a convention dating back to vacuum tubes), like this: 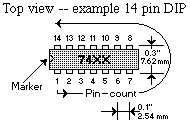 |
|
|
|
Manufacturers are also good sources of IC
package information -- Oki has an exhaustive page
here,
while Hitachi has a more-concise one here. |
|
|
||
|
|
This page was last updated on |
|